pytorch日积月累1-张量数据类型
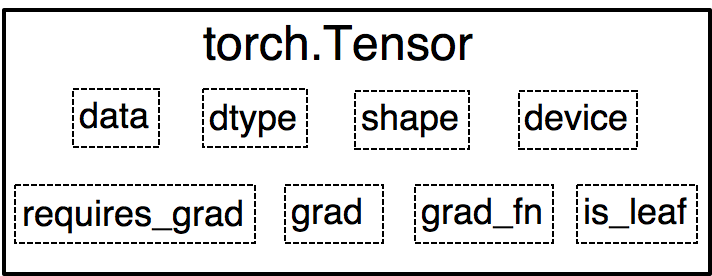
张量是一个多维数组,它是标量、向量、矩阵的高维拓展。
Variable是torch.autograd中的数据类型,主要用于封装Tensor,进行自动求导
PyTorch 0.4.0版开始,Variable并入Tensor
dtype : 张量的数据类型,如 torch .FloatTensor, torch .cuda.FloatTensor
shape : 张量的形状,如( 64 , 3 , 224 , 224 )
device : 张量所在设备,GPU/CPU,是加速的关键
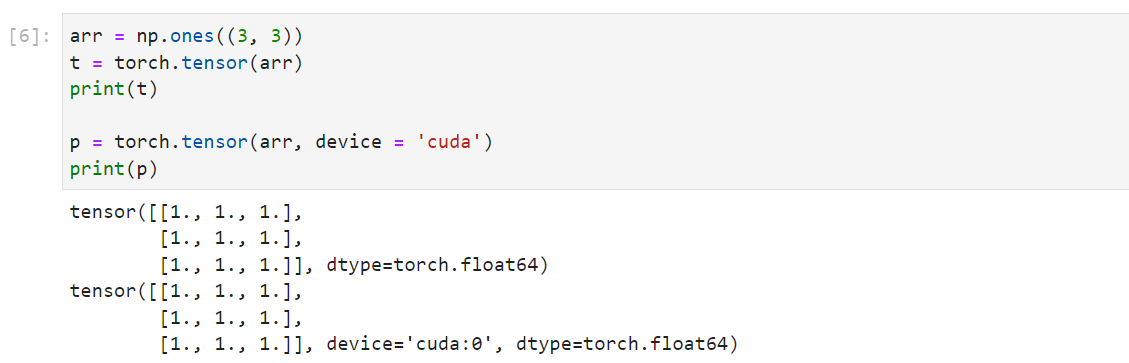
1.直接创建
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import torch
arr = np.ones((3, 3))
torch.tensor(
data,
dtype=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False,
pin_memory=False
)
|
numpy引入法
torch.from_numpy (ndarray)
功能:从numpy创建tensor
注意事项:从torch.from_numpy创建的tensor于原ndarray共享内存,当修改其中一个的数据,另外一个也将会被改动
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import numpy as np
import torch
a=np.array([2,3.3])
torch.from_numpy(a)
a=np.ones([2,3])
torch.from_numpy(a)
|
2.依据数值创建
1
2
3
4
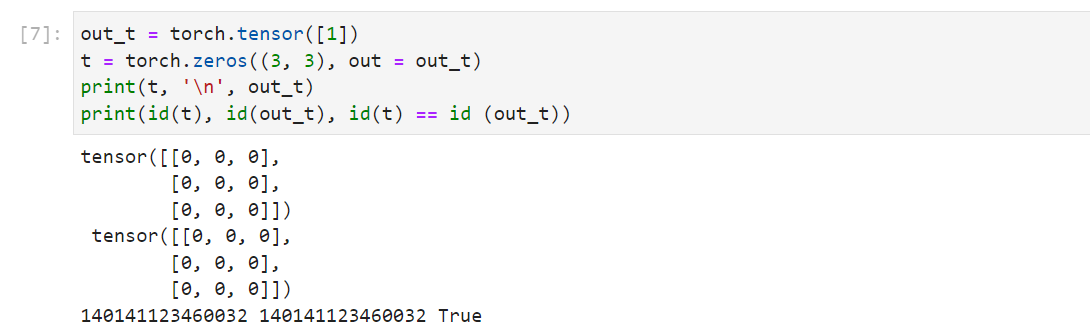
| torch.zeros(*size, out=None, dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.zeros_like(input, dtype=None, layout=None, device=None,
requires_grad=False)
|
1
2
3
4
| torch.ones(*size, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided,
device=None, requires_grad=False
torch.ones_like(input, dtype=None, layout=None, device=None,
requires_grad=False)
|
1
2
| torch.full( size, fill_value, out=None, dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
|
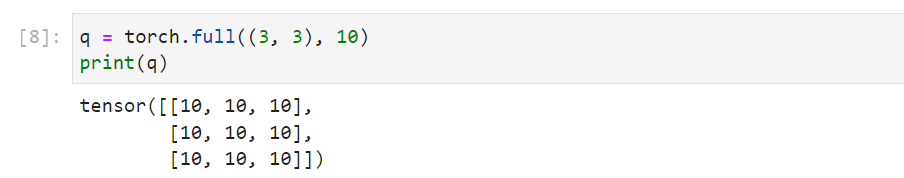
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
torch.arange(start=0,
end,
step=1,
out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided,
device=None, requires_grad=False)
|
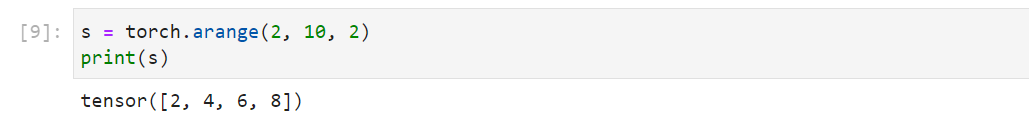
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
torch.linspace(start,
end,
steps=100,
out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided,
device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.logspace(start,
end,
steps=100,
base=10.0,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
|

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| torch.eye(
n,
m=None,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
|
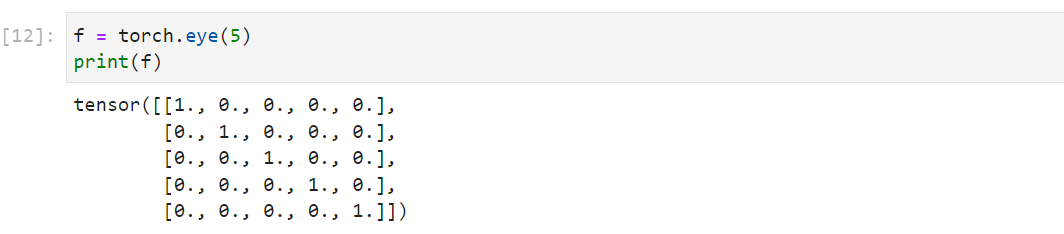
3.依据概率分布创建
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
torch.normal(mean,std, out=None)
torch.randn(*size, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided,
device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.rand(*size, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided,
device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.randint(low=0,
high, size, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided,
device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.randperm(n,out=None,dtype=torch.int64,layout=torch.strided,
device=None,requires_grad=False)
torch.bernoulli(input, *, generator=None, out=None)
|

List引入法
1
2
3
4
5
| import numpy as np
import torch
torch.tensor([2.,3.2])
torch.FloatTensor([2.,3.2])
torch.tensor([[2.,3.2],[1.,22.3]])
|
未初始化数据
torch.empty()
torch.FloatTensor(d1,d2,d3)注意:这里不是torch.FloatTensor([1,2])=torch.tensor([1,2])
Torch.IntTensor(d1,d2,d3)
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import numpy as np
import torch
torch.empty(1)
torch.Tensor(2,3)
torch.IntTensor(2,3)
torch.FloatTensor(2,3)
|
一个小技巧:设置对应的Tensor格式:
1
2
3
4
|
torch.tensor([1.2,3]).type()
torch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.DoubleTensor)
torch.tensor([1.2,3]).type()
|








