pytorch日积月累2-张量操作 1.索引与切片 1 2 3 4 5 a=torch.rand(4 ,3 ,28 ,28 ) a[0 ].shape a[0 ,0 ].shape a[0 ,0 ,2 ,4 ]
沿用python中的索引方法:start:end:step
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a=torch.rand(4 ,3 ,28 ,28 ) a[:2 ].shape a[:2 ,:1 ,:,:].shape a[:2 ,1 :,:,:].shape a[:2 ,-1 :,:,:].shape a[:,:,0 :28 :2 ,0 :28 :2 ].shape a[:,:,::2 ,::2 ].shape
根据特殊的索引来进行采样:
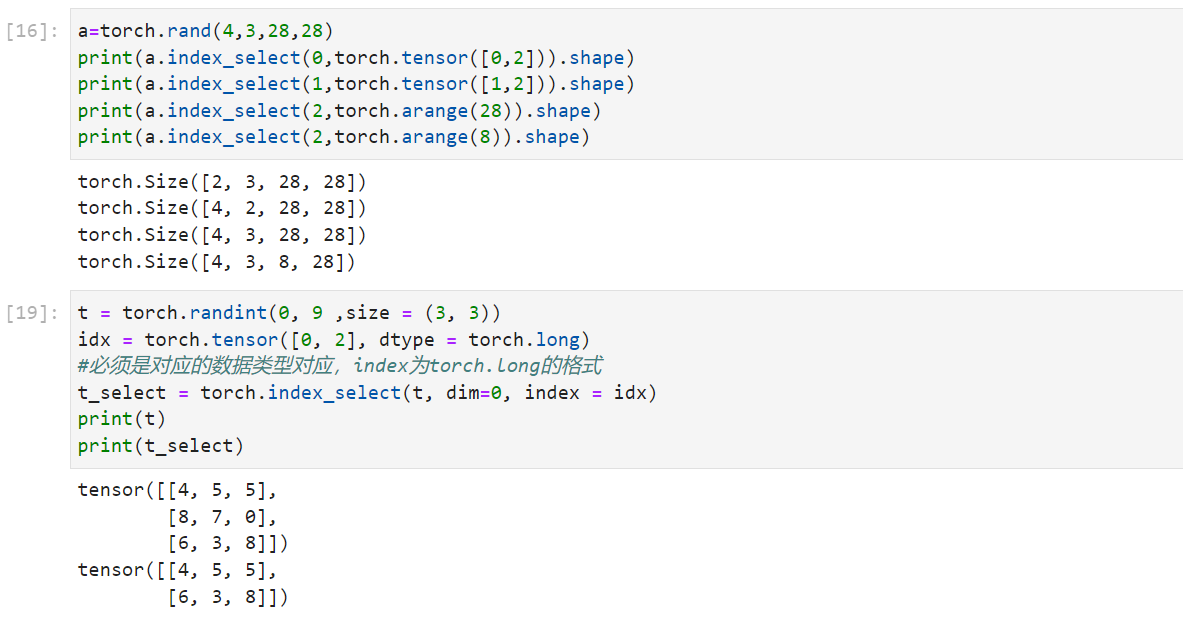
1 2 3 4 5 a=torch.rand(4 ,3 ,28 ,28 ) a.index_select(0 ,torch.tensor([0 ,2 ])).shape a.index_select(1 ,torch.tensor([1 ,2 ])).shape a.index_select(2 ,torch.arange(28 )).shape a.index_select(2 ,torch.arange(8 )).shape
特殊的切片符号...,为了方便与: :的表示法相同
1 2 3 4 5 6 a.shape a[...].shape a[0 ,...].shape a[:,1 ,...].shape a[...,:2 ].shape
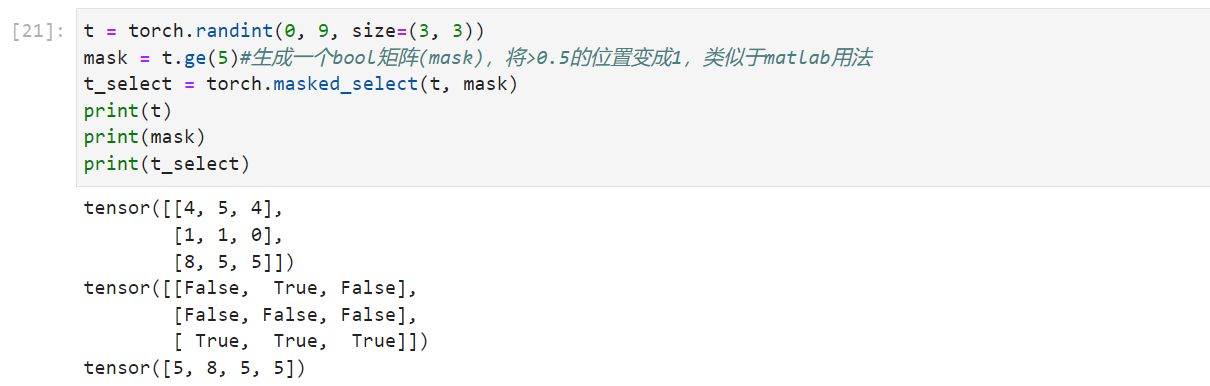
根据mask来选择:按照mask中的True序列进行索引
1 2 3 4 5 6 t = torch.randint(0 , 9 , size=(3 , 3 )) mask = t.ge(5 ) t_select = torch.masked_select(t, mask) print (t)print (mask)print (t_select)
select by flatten index
1 2 src=torch.tensor([[4 ,3 ,5 ],[6 ,7 ,8 ]]) torch.take(src,torch.tensor([0 ,2 ,5 ]))
2.维度变换
View/reshape操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 t=torch.randperm(8 ) t_reshape=torch.reshape(t,(2 ,4 )) print ("t:{}\nt_reshape:\n{}" .format (t,t_reshape))t[0 ]=1024 print ("t:{}\nt_reshape:\n{}" .format (t,t_reshape))print ("t.data 内存地址:{}" .format (id (t.data)))print ("t_reshape.data 内存地址:{}" .format (id (t_reshape.data)))
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a=torch.rand(4 ,1 ,28 ,28 ) a.view(4 ,28 *28 ) a.view(4 ,28 *28 ).shape a.view(4 *28 ,28 ).shape a.view(4 *1 ,28 ,28 ).shape b=a.view(4 ,784 ) b.view(4 ,28 ,28 ,1 )
Squeeze/unsqueeze操作 :unsqueeze(pos\index)
功能:压缩长度为1的维度(轴)
torch.squeeze(input, dim=None, out=None)
dim:若为None,移除所有长度为1的轴,若指定维度,当且仅当该轴长度为1时,可以被移除。
注意:[-a.dim()-1,a.dim()+1)
1 2 3 4 5 t = torch.rand((1 , 2 , 3 , 1 )) t_sq = torch.squeeze(t) t_0 = torch.squeeze(t, dim=0 ) t_1 = torch.squeeze(t, dim=1 ) print (t.shape, t_sq.shape, t_0.shape, t_1.shape)
torch.unsqueeze(input, dim=None, out=None)功能:依据dim扩展维度。dim:指定扩展的维度
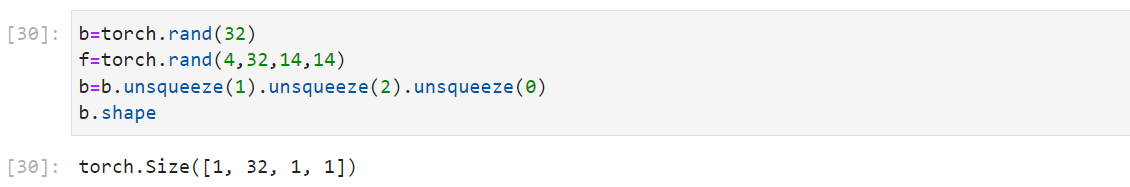
实际的应用,在图像处理的过程中添加偏置项:
1 2 3 4 b=torch.rand(32 ) f=torch.rand(4 ,32 ,14 ,14 ) b=b.unsqueeze(1 ).unsqueeze(2 ).unsqueeze(0 ) b.shape
squeeze(pos\index)如果不设置索引,会将所有的维度全部收缩挤压
1 2 3 4 5 b.shape b.squeeze().shape b.squeeze(0 ).shape b.squeeze(-1 ).shape b.squeeze(1 ).shape
Expand/repeat
Expand:broadcasting
Repeat:memory copied
1 2 3 4 5 a=torch.rand(4 ,32 ,14 ,14 ) b.shape b.expand(4 ,32 ,14 ,14 ).shape b.expand(-1 ,32 ,-1 ,-1 ).shape b.expand(-1 ,32 ,-1 ,-4 ).shape
1 2 3 4 5 b.shape b.repeat(4 ,32 ,1 ,1 ).shape b.repeat(4 ,1 ,1 ,1 ).shape b.repeat(4 ,1 ,32 ,32 ).shape
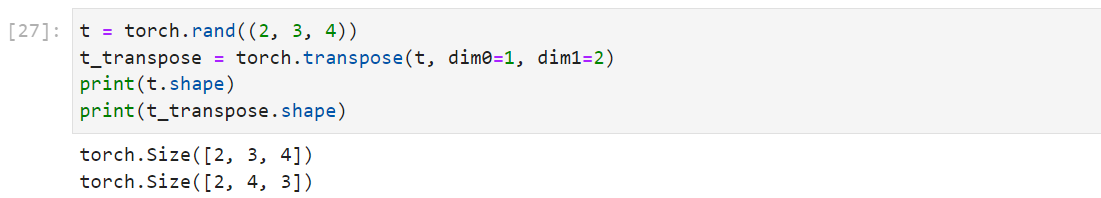
转置操作
1 2 3 4 t = torch.rand((2 , 3 , 4 )) t_transpose = torch.transpose(t, dim0=1 , dim1=2 ) print (t.shape)print (t_transpose.shape)
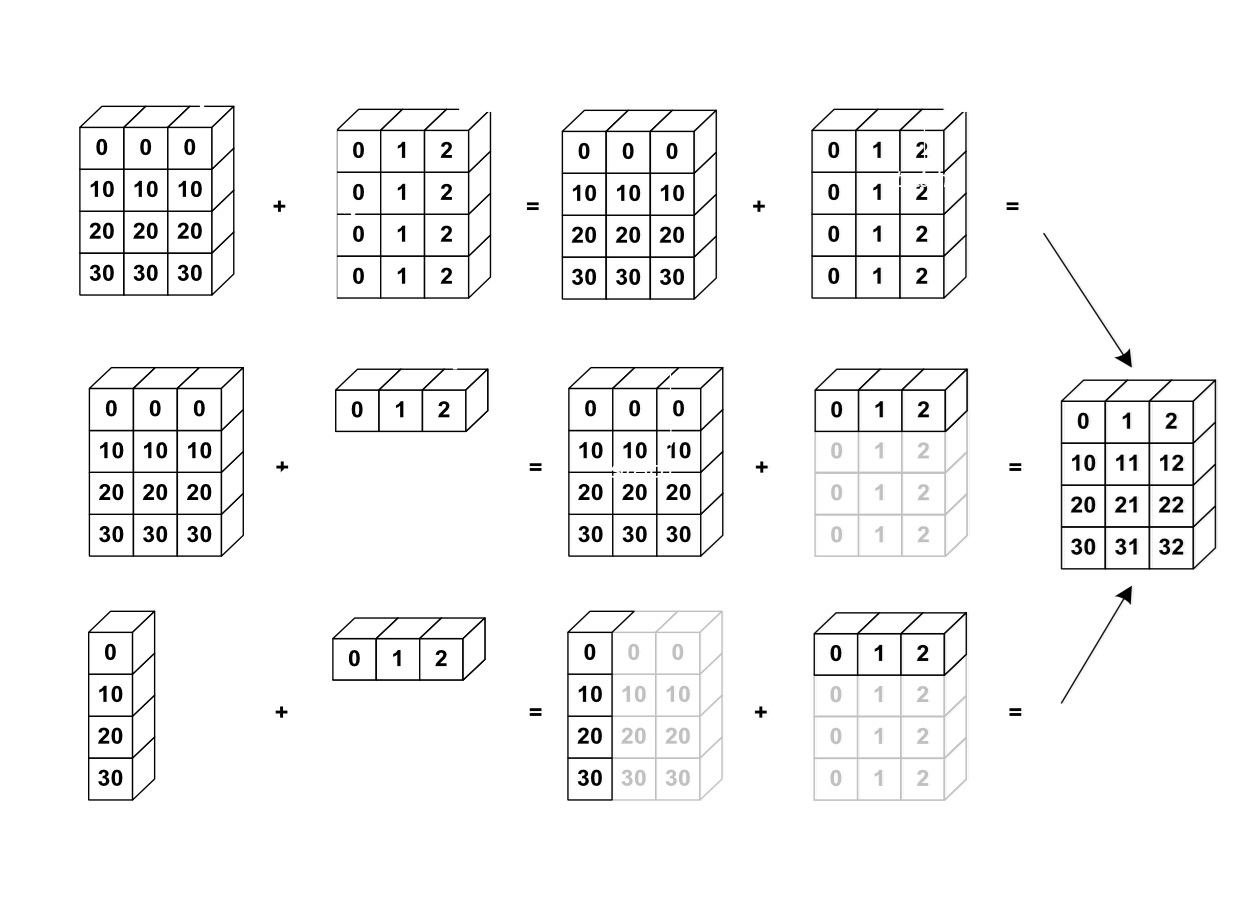
3.Broadcasting自动扩张 Expand:without copying data
Key idea
Insert 1 dim ahead Expand dims with size 1 to same size
Feature maps: [4, 32, 14, 14] Bias: [32, 1, 1] => [1, 32, 1, 1] => [4, 32, 14, 14]
自动扩张 :先添加1维,再扩展数据
Is it broadcasting-able?
▪ Match from Last dim!
▪ If current dim=1, expand to same
▪ If either has no dim, insert one dim and expand to same
▪ otherwise, NOT broadcasting-able
小维度指定,大维度随意
4.拼接与拆分 Merge or split
▪ Cat ▪ Stack ▪ Split ▪ Chunk
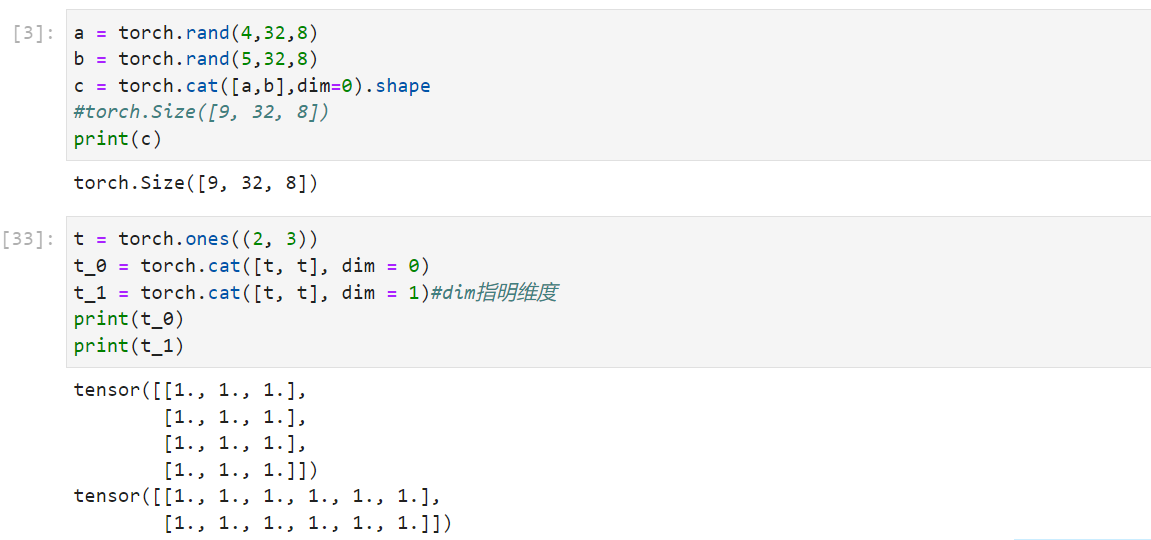
cat: 必须保证除了拼接维度以外的维度都要相等
1 2 3 4 a=torch.rand(4 ,32 ,8 ) b=torch.rand(5 ,32 ,8 ) torch.cat([a,b],dim=0 ).shape
stack :插入一个新的维度create new dim
1 2 3 4 a=torch.rand(4 ,32 ,8 ,8 ) b=torch.rand(4 ,32 ,8 ,8 ) torch.stack([a,b],dim=2 ).shape
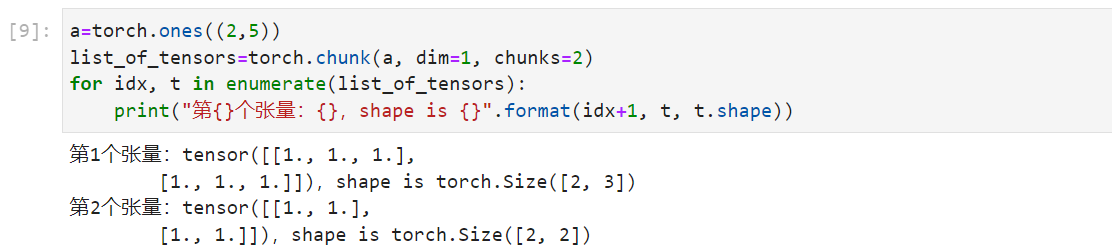
chunk: 将张量按照维度dim进行平均切分,返回值为张量列表
注意:如果不能整除,最后一份张量小于其他的张量。
1 2 3 4 a=torch.ones((2 ,5 )) list_of_tensors=torch.chunk(a,dim=1 ,chunks=2 ) for idx,t in enumerate (list_of_tensors): print ("第{}个张量:{},shape is {}" .format (idx+1 ,t,t.shape))
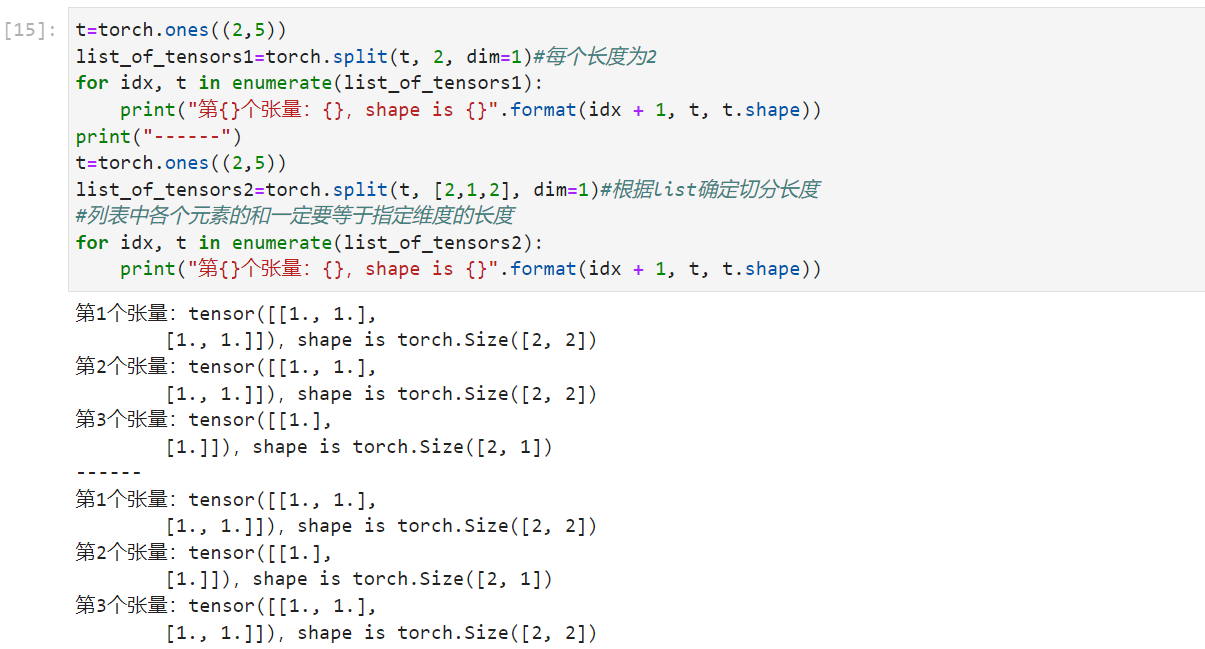
split: 将张量按维度dim进行切分,返回值为张量列表
torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0)
split_size_or_sections:为int时,表示每一份的长度,为list时,按list元素切分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 t=torch.ones((2 ,5 )) list_of_tensors1=torch.split(t,2 ,dim=1 ) for idx,t in enumerate (list_of_tensors1): print ("第{}个张量:{},shape is {}" .format (idx+1 ,t,t.shape)) list_of_tensors2=torch.split(t,[2 ,1 ,2 ],dim=1 ) for idx,t in enumerate (list_of_tensors2): print ("第{}个张量:{},shape is {}" .format (idx+1 ,t,t.shape))
5.数学运算 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 torch.add() torch.addcdiv() torch.addcmul() torch.sub() torch.div() torch.mul() torch.log(input , out=None ) torch.log10(input , out=None ) torch.log2(input , out=None ) torch.exp(input , out=None ) torch.pow () torch.abs (input , out=None ) torch.acos(input , out=None ) torch.cosh(input , out=None ) torch.cos(input , out=None ) torch.asin(input , out=None ) torch.atan(input , out=None ) torch.atan2(input , other, out=None ) torch.mm(a,b) torch.matmul(a,b) a@b
为了便于深度学习的进行pytorch封装了一些内置的特殊用法:
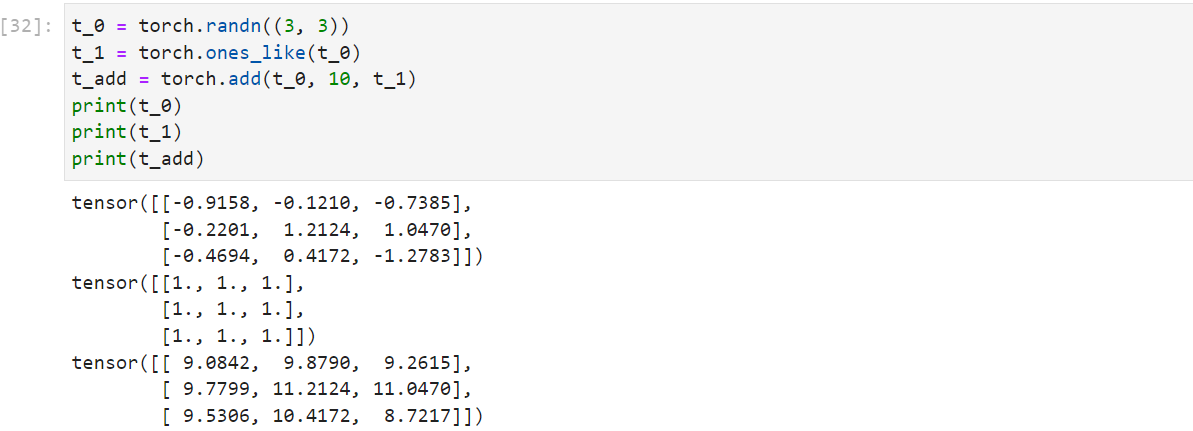
1 torch.add(input , alpha=1 , other, out=None )
torch.addcdiv():
torch.addcmul():
1 torch.addcmul(input , value=1 , tensor1, tensor2,out=None )
1 2 3 4 5 6 t_0 = torch.randn((3 , 3 )) t_1 = torch.ones_like(t_0) t_add = torch.add(t_0, 10 , t_1) print (t_0)print (t_1)print (t_add)


 Is it broadcasting-able?
Is it broadcasting-able?