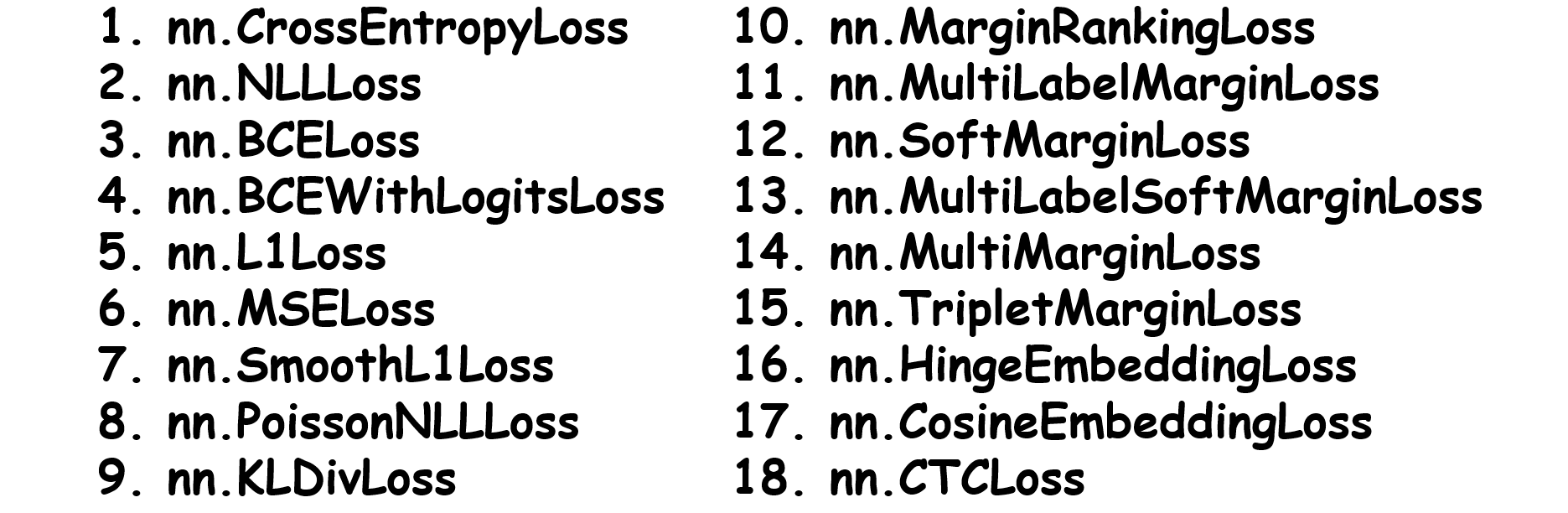
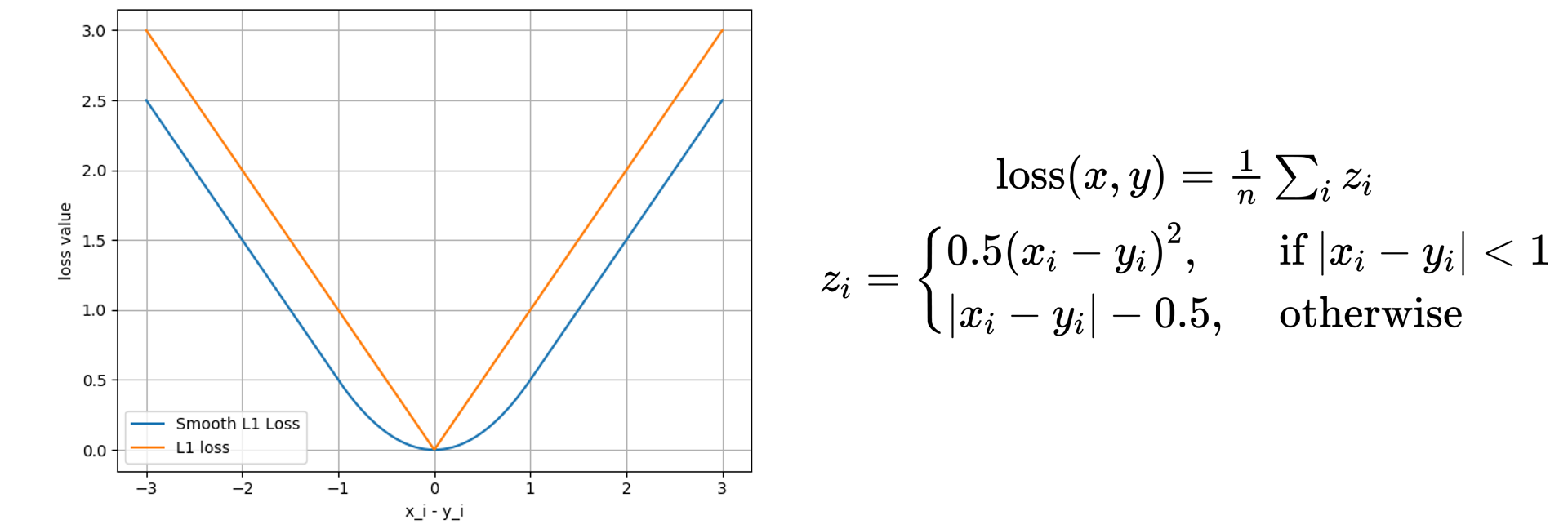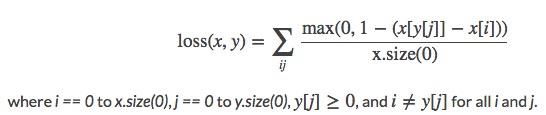pytorch日积月累9-损失函数
损失函数:衡量模型输出与真实标签的差异
损失函数(Loss Function):
代价函数(Cost Function):
目标函数(Objective Function):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| class _Loss(Module):
def __init__(self, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean'):
super(_Loss, self).__init__()
if size_average is not None or reduce is not None:
self.reduction = _Reduction.legacy_get_string(
size_average, reduce)
else:
self.reduction = reduction
|
1.交叉熵损失函数
功能: nn.LogSoftmax ()与nn.NLLLoss ()结合,进行交叉熵计算
主要参数:
熵:
自信息:
相对熵:
交叉熵:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None,
size_average=None,
ignore_index=-100,
reduce=None,
reduction=‘mean’)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
loss_f_none = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, reduction='none')
loss_none = loss_f_none(inputs, target)
print("Cross Entropy Loss:\n ", loss_none, loss_sum, loss_mean)
idx = 0
input_1 = inputs.detach().numpy()[idx]
target_1 = target.numpy()[idx]
x_class = input_1[target_1]
sigma_exp_x = np.sum(list(map(np.exp, input_1)))
log_sigma_exp_x = np.log(sigma_exp_x)
loss_1 = -x_class + log_sigma_exp_x
print("第一个样本loss为: ", loss_1)
weights = torch.tensor([1, 2], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_none_w = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=weights, reduction='none')
|
2.NLLLoss
功能:实现负对数似然函数中的负号功能
1
2
3
4
5
| nn.NLLLoss( weight=None,
size_average=None,
ignore_index=-100,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
3.BCELoss
功能:二分类交叉熵
注意事项:输入值取值在[0,1]
主要参数:
1
2
3
4
| nn.BCELoss( weight=None,
size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| inputs = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [2, 2], [3, 4], [4, 5]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([[1, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], [0, 1]], dtype=torch.float)
target_bce = target
inputs = torch.sigmoid(inputs)
weights = torch.tensor([1, 1], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_none_w = nn.BCELoss(weight=weights, reduction='none')
loss_none_w = loss_f_none_w(inputs, target_bce)
|
4.BCEWithLogitsLoss
功能:结合Sigmoid与二分类交叉熵
注意事项:网络最后不加sigmoid函数
1
2
3
4
5
| nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=None,
size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean',
pos_weight=None)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| inputs = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [2, 2], [3, 4], [4, 5]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([[1, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], [0, 1]], dtype=torch.float)
target_bce = target
weights = torch.tensor([1], dtype=torch.float)
pos_w = torch.tensor([3], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_none_w = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=weights, reduction='none',
pos_weight=pos_w)
loss_none_w = loss_f_none_w(inputs, target_bce)
|
5.nn.L1Loss
功能: 计算inputs与target之差的绝对值
1
2
3
| nn.L1Loss(size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean’)
|
6.nn.MSELoss
功能: 计算inputs与target之差的平方
1
2
3
| nn.MSELoss(size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean’)
|
7.SmoothL1Loss
功能: 平滑的L1Loss
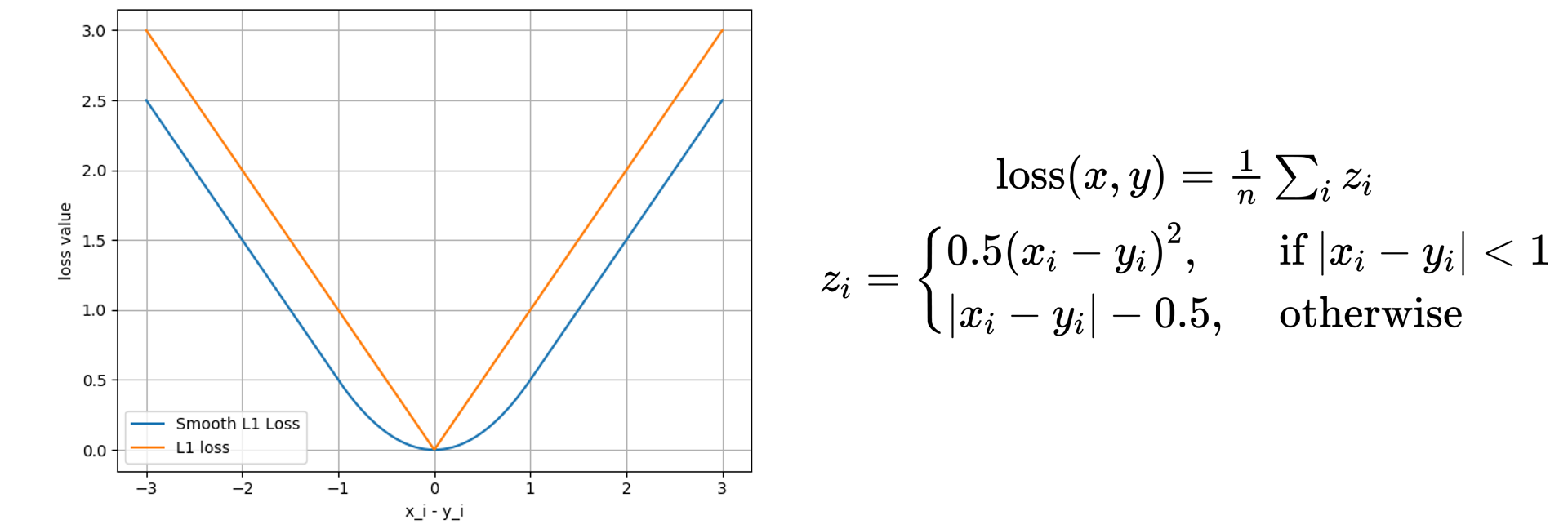
1
2
3
| nn.SmoothL1Loss(size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean’)
|
8.PoissonNLLLoss
功能:泊松分布的负对数似然损失函数
log_input = True:loss(input, target) = exp(input) - target * input
log_input = False:loss(input, target) = input - target * log(input+eps)
1
2
3
4
5
6
| nn.PoissonNLLLoss(log_input=True,
full=False,
size_average=None,
eps=1e-08,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
9.nn.KLDivLoss
功能:计算KLD(divergence),KL散度,相对熵
注意事项:需提前将输入计算 log-probabilities,如通过nn.logsoftmax()
1
2
3
4
5
| nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| inputs = torch.tensor([[0.5, 0.3, 0.2], [0.2, 0.3, 0.5]])
inputs_log = torch.log(inputs)
target = torch.tensor([[0.9, 0.05, 0.05], [0.1, 0.7, 0.2]],
dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_bs_mean = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='batchmean')
loss_bs_mean = loss_f_bs_mean(inputs, target)
|
10.nn.MarginRankingLoss
功能:计算两个向量之间的相似度,用于排序任务
特别说明:该方法计算两组数据之间的差异,返回一个的 loss 矩阵
1
2
3
4
5
6
| nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0.0,
size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| x1 = torch.tensor([[1], [2], [3]], dtype=torch.float)
x2 = torch.tensor([[2], [2], [2]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([1, 1, -1], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_none = nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0, reduction='none')
loss = loss_f_none(x1, x2, target)
print(loss)
|
11.nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss
功能:多标签边界损失函数
举例:四分类任务,样本x属于0类和3类,标签:[0, 3, -1, -1] , 不是[1, 0, 0, 1]
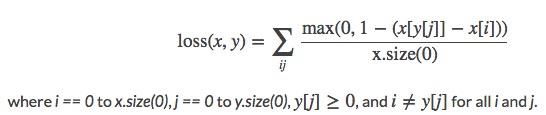
1
2
3
4
| nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss(
size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| x = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8]])
y = torch.tensor([[0, 3, -1, -1]], dtype=torch.long)
loss_f = nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss(reduction='none')
loss = loss_f(x, y)
x = x[0]
item_1 = (1-(x[0] - x[1])) + (1 - (x[0] - x[2]))
item_2 = (1-(x[3] - x[1])) + (1 - (x[3] - x[2]))
loss_h = (item_1 + item_2) / x.shape[0]
print(loss_h)
|
12.nn.SoftMarginLoss
功能:计算二分类的logistic损失
1
2
3
| nn.SoftMarginLoss(size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
13.nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss
功能:SoftMarginLoss多标签版本
1
2
3
4
| nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss(weight=None,
size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
14.nn.MultiMarginLoss
功能:计算多分类的折页损失

1
2
3
4
5
6
| nn.MultiMarginLoss(p=1,
margin=1.0,
weight=None,
size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
15.nn.TripletMarginLoss
功能:计算三元组损失,人脸验证中常用
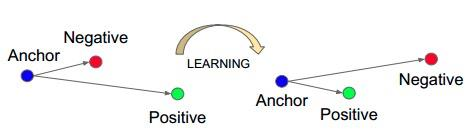
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0,
p=2.0,
eps=1e-06,
swap=False,
size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
16.nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss
功能:计算两个输入的相似性,常用于非线性embedding和半监督学习
特别注意:输入x应为两个输入之差的绝对值。
1
2
3
4
| nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=1.0,
size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean’)
|
1
2
3
4
5
| inputs = torch.tensor([[1., 0.8, 0.5]])
target = torch.tensor([[1, 1, -1]])
loss_f = nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=1, reduction='none')
loss = loss_f(inputs, target)
print("Hinge Embedding Loss", loss)
|
17.nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss
功能:采用余弦相似度计算两个输入的相似性
1
2
3
4
| nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss(margin=0.0,
size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
|
18.nn.CTCLoss
功能: 计算CTC损失,解决时序类数据的分类
Connectionist Temporal Classification
1
2
3
| torch.nn.CTCLoss(blank=0,
reduction='mean',
zero_infinity=False)
|